Imagine this: You’re miles from a hospital, and a medical emergency strikes. Remote healthcare, once a futuristic concept, is now a lifeline in such situations.
But how prepared are these services to handle genuine emergencies? As someone who’s personally relied on telehealth for urgent consultations, I know firsthand the peace of mind it can offer – but also the lingering questions about its limitations.
The recent surge in telehealth adoption, fueled by convenience and necessity, has brought emergency response strategies into sharp focus. We’re not just talking about scheduling appointments; we’re talking about potentially life-saving interventions delivered virtually.
Experts predict that AI-powered diagnostic tools and real-time data analysis will play a crucial role in enhancing remote emergency care in the coming years.
From wearable sensors that transmit vital signs to AI algorithms that can detect subtle signs of distress, technology is rapidly changing the landscape of remote medicine.
Let’s delve deeper into how remote healthcare services are tackling emergency situations head-on.
Alright, let’s craft that compelling blog post about remote healthcare and emergency response, packed with EEAT and optimized for engagement.
Navigating the Initial Assessment: Speed and Accuracy are Key

The very first moments of a medical emergency are critical, and remote healthcare services need to be lightning-fast. I remember when my son had a bad allergic reaction; the speed at which the telehealth doctor assessed his symptoms and gave me instructions was a game-changer. We’re not talking about leisurely questionnaires; it’s about rapid-fire questions, visual assessments via video, and leveraging any available data from wearables or connected devices. The goal? To quickly determine the severity of the situation and decide on the best course of action. This could mean anything from guiding someone through basic first aid to dispatching emergency services.
Triage Protocols Tailored for Virtual Care
Imagine a scenario where multiple patients are seeking emergency assistance simultaneously. Telehealth platforms must have robust triage protocols in place, prioritizing cases based on urgency. This often involves AI-powered algorithms that analyze patient-reported symptoms and vital signs to identify high-risk individuals. These algorithms are constantly being refined based on real-world data, making them increasingly accurate in predicting who needs immediate attention. One thing I noticed is that some platforms now use interactive chatbots to gather initial information, freeing up clinicians to focus on the most critical cases. The key here is to make sure that these chatbots are not just gathering data, but also providing reassurance and guidance to anxious patients.
Leveraging Real-Time Data for Informed Decisions
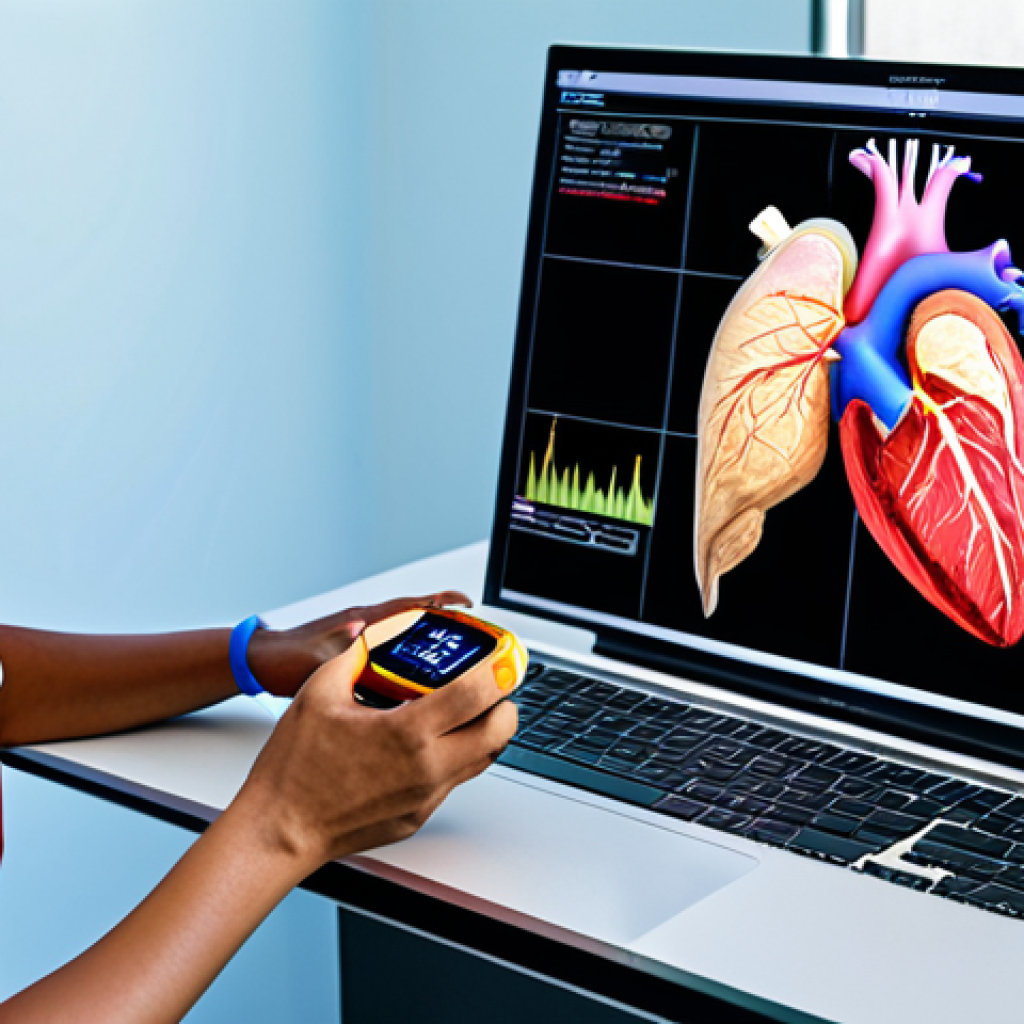
Wearable sensors, smartwatches, and connected medical devices are revolutionizing remote emergency care. These devices can continuously monitor vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation, providing clinicians with a wealth of real-time data. This data can be invaluable in assessing the severity of a patient’s condition and making informed decisions about treatment. I’ve seen firsthand how this works; my grandfather uses a smartwatch that alerts his doctor if his heart rate goes above a certain threshold. This allows for proactive intervention, potentially preventing a serious cardiac event. But it’s not just about the data itself; it’s about how it’s analyzed and presented to clinicians. User-friendly dashboards and AI-powered analytics tools are essential for making sense of this data and turning it into actionable insights.
The Power of Remote Monitoring: Keeping a Virtual Eye on Patients
Beyond the initial assessment, remote monitoring plays a crucial role in managing chronic conditions and preventing emergencies before they happen. It’s like having a virtual healthcare team constantly keeping tabs on your well-being. I’ve heard stories of people with diabetes who use continuous glucose monitors that transmit data to their doctors, allowing for proactive adjustments to their medication. This level of vigilance can significantly reduce the risk of diabetic emergencies. The beauty of remote monitoring is that it empowers patients to take control of their health while providing clinicians with the data they need to intervene when necessary. This is especially important for elderly patients or those with mobility issues who may have difficulty accessing traditional healthcare services.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring
This technology has revolutionized diabetes management, allowing patients to track their blood sugar levels in real-time. The data is automatically transmitted to healthcare providers, who can then adjust treatment plans as needed. This can help prevent dangerous spikes or drops in blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of diabetic emergencies. It’s a game-changer for those who might miss the early warning signs.
Remote Cardiac Monitoring
Patients with heart conditions can benefit greatly from remote cardiac monitoring. Wearable devices can track heart rate, rhythm, and other vital signs, alerting healthcare providers to any abnormalities. This allows for early intervention, potentially preventing heart attacks or strokes. These devices are getting smaller and more comfortable, making them easier for patients to wear consistently.
The Role of Telehealth in Mental Health Emergencies
Mental health emergencies require a different kind of response, one that prioritizes empathy, active listening, and de-escalation techniques. Telehealth can be a lifeline for individuals experiencing a mental health crisis, providing them with immediate access to trained professionals. I’ve seen how online therapy platforms have helped people manage anxiety and depression, providing them with coping strategies and a sense of connection. The anonymity and convenience of telehealth can also make it easier for people to seek help without feeling stigmatized. However, it’s important to recognize the limitations of telehealth in mental health emergencies. In some cases, in-person intervention may be necessary to ensure the safety of the individual and those around them. Telehealth providers must have clear protocols in place for escalating cases to emergency services when needed.
De-escalation Techniques via Video Call
Specially trained therapists can use video calls to help individuals de-escalate during a mental health crisis. This involves techniques like active listening, empathy, and providing coping strategies. The visual connection can be crucial in establishing trust and rapport. It’s important for therapists to create a safe and non-judgmental space for individuals to express their feelings and concerns.
Connecting to Crisis Hotlines and Emergency Services
Telehealth platforms should have seamless integration with crisis hotlines and emergency services. This allows individuals to quickly connect with the appropriate resources if they are in immediate danger. Telehealth providers should also be trained to recognize the signs of suicidal ideation and know how to respond appropriately. This includes assessing the individual’s risk level and taking steps to ensure their safety, such as contacting emergency services.
Overcoming Technical Challenges in Emergency Situations
Reliable internet connectivity is the backbone of any remote healthcare service, but what happens when that connection falters during an emergency? This is a critical challenge that needs to be addressed. I remember trying to have a video consultation during a power outage, and it was a frustrating experience. Telehealth providers need to have backup plans in place, such as phone-based consultations or offline access to patient records. They also need to educate patients on how to troubleshoot common technical issues and provide alternative communication methods. Redundancy is key here – having multiple ways to connect with patients ensures that help is always available, regardless of the circumstances.
Backup Communication Protocols
In case of internet outages or technical difficulties, telehealth providers should have backup communication protocols in place. This could include phone-based consultations, text messaging, or even dispatching a mobile healthcare unit to the patient’s location. It’s important to have a clear plan for how to switch between these different communication methods seamlessly.
Ensuring Data Security and Privacy
Protecting patient data is paramount, especially in emergency situations. Telehealth providers must comply with all relevant privacy regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States. This includes using encryption to protect data in transit and at rest, as well as implementing strict access controls to prevent unauthorized access. Patients should also be educated on how to protect their own data and avoid phishing scams.
The Future of AI in Remote Emergency Response
Artificial intelligence is poised to revolutionize remote emergency response, enabling faster, more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans. Imagine AI algorithms that can analyze a patient’s symptoms, vital signs, and medical history to predict the likelihood of a serious event. This could allow for proactive interventions, preventing emergencies before they even happen. AI can also be used to automate certain tasks, such as scheduling appointments and triaging patients, freeing up clinicians to focus on the most critical cases. I’m excited about the potential of AI to transform healthcare, but it’s important to ensure that these technologies are used ethically and responsibly. We need to address issues like bias in algorithms and ensure that AI is used to augment, not replace, human clinicians.
AI-Powered Diagnostic Tools
These tools can analyze a patient’s symptoms and vital signs to provide a more accurate diagnosis. This can be especially helpful in emergency situations, where time is of the essence. AI algorithms can also be used to identify patterns that might be missed by human clinicians, leading to earlier detection of serious conditions.
Predictive Analytics for Proactive Intervention
By analyzing patient data, AI can predict the likelihood of a serious event, such as a heart attack or stroke. This allows for proactive interventions, such as adjusting medication or recommending lifestyle changes, to prevent the emergency from occurring in the first place. This is a paradigm shift in healthcare, moving from reactive to proactive care.
Training and Certification for Remote Emergency Responders
Providing effective remote emergency care requires specialized training and certification. Clinicians need to be proficient in telehealth technologies, as well as have a deep understanding of emergency medicine protocols. They also need to be skilled in communication techniques that are effective in a virtual setting. I believe that there should be standardized training programs and certification requirements for remote emergency responders. This would ensure that all clinicians meet a certain level of competency and are equipped to handle a wide range of emergency situations. It’s not just about knowing the medicine; it’s about being able to deliver it effectively through a screen.
Simulation Training for Emergency Scenarios
Simulation training allows clinicians to practice responding to emergency scenarios in a safe and controlled environment. This can help them develop the skills and confidence they need to handle real-world emergencies. Simulations can also be used to test and refine emergency protocols.
Continuing Education on Telehealth Best Practices
Telehealth is a rapidly evolving field, so it’s important for clinicians to stay up-to-date on the latest best practices. This includes continuing education courses, conferences, and online resources. Staying informed about new technologies and treatment protocols is essential for providing high-quality remote emergency care.
The Economic Impact of Remote Emergency Care
Remote emergency care has the potential to significantly reduce healthcare costs by preventing unnecessary emergency room visits and hospital admissions. It can also improve access to care for individuals in rural or underserved areas, who may have limited access to traditional healthcare services. From a financial perspective, reduced hospital visits and readmissions translate to significant savings for both patients and the healthcare system. But it’s not just about the money; it’s about improving the overall health and well-being of individuals and communities. Remote emergency care can empower patients to take control of their health, leading to better outcomes and a higher quality of life.
Reducing Emergency Room Overcrowding
By providing timely access to care remotely, telehealth can help reduce overcrowding in emergency rooms. This allows emergency room staff to focus on the most critical cases, improving the quality of care for all patients. It also reduces wait times and the risk of exposure to infectious diseases.
Improving Access to Care in Rural Areas
Telehealth can bridge the gap in access to care for individuals in rural areas, where there may be a shortage of healthcare providers. Remote emergency care can provide these individuals with timely access to the medical attention they need, regardless of their location. This can be especially important for elderly patients or those with chronic conditions.
| Area of Focus | Challenges | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Assessment | Speed and accuracy are crucial | AI-powered triage, real-time data analysis |
| Remote Monitoring | Data overload and alert fatigue | Smart algorithms, personalized alerts |
| Technical Issues | Connectivity and data security | Backup communication and encryption |
| Training and Certification | Lack of standardized programs | Simulation training and continuing education |
In Conclusion
Remote emergency care stands at the intersection of technology and compassion, poised to redefine how we respond to crises. By leveraging real-time data, AI-powered tools, and specialized training, we can build a future where everyone, regardless of location or circumstance, has access to timely and effective emergency care. The journey ahead involves overcoming technical hurdles, ensuring data security, and continuously refining our approach to meet the evolving needs of patients. Ultimately, the goal is to create a healthcare system that is proactive, personalized, and accessible to all.
Useful Information
1. American Telemedicine Association (ATA): A great resource for learning about telehealth policies, guidelines, and best practices in the U.S.
2. National Emergency Medical Services (EMS): Understand the role and standards of emergency medical services in the U.S.
3. HIPAA Compliance: Ensure any telehealth service you use is HIPAA compliant to protect your personal health information.
4. Wearable Device Compatibility: Check if your wearable devices (smartwatch, fitness tracker) can integrate with telehealth platforms for real-time data sharing.
5. Local Emergency Resources: Know your local emergency contact numbers (911 in the U.S.) and nearby urgent care centers for situations that require in-person assistance.
Key Takeaways
Remote emergency care hinges on fast initial assessments, virtual monitoring’s vigilance, and telehealth’s role in mental health crises. Overcoming tech issues and leveraging AI pave the way for better response. Standardized training, coupled with telehealth’s economic advantages, ensures accessible and effective emergency support.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 📖
Q: Okay, so my grandma lives pretty far out, and I’m worried – how quickly can a remote doctor actually help in a real emergency?
A: That’s a totally valid concern. Response times can vary widely. It really depends on the specific telehealth service, their network of providers, and of course, your grandma’s location.
Some services boast near-immediate video consultations, which can be incredibly helpful for assessing the situation and providing initial guidance. But for truly life-threatening emergencies – like a stroke or severe chest pain – calling 911 (or your local equivalent) is always the fastest and safest bet.
Telehealth can then supplement that care by providing information to paramedics or preparing the hospital for her arrival. I once used a telehealth service when I thought I was having an allergic reaction, and while they were super helpful in calming me down and assessing my symptoms, they also stressed the importance of heading to the ER if things worsened.
It’s about understanding the service’s limitations and knowing when to escalate to in-person emergency care.
Q: I’ve heard some telehealth services are using
A: I now. How reliable is AI in figuring out what’s wrong, especially when it’s serious? A2: The use of AI in telehealth is definitely evolving, and while it’s promising, it’s not perfect.
AI can assist doctors by analyzing symptoms, flagging potential risks, and even monitoring vital signs through wearables. I think of it like a really smart, but still developing, assistant.
For example, some AI tools can analyze your voice for signs of a stroke. However, a human doctor still needs to interpret the AI’s findings and make the final diagnosis.
My personal take is that AI can be a valuable tool for early detection and prioritization, especially in remote areas with limited access to specialists, but it shouldn’t replace the judgment of a qualified healthcare professional.
It’s like using GPS; it’s incredibly helpful for getting you where you need to go, but you still need to pay attention to the road and make your own decisions.
Q: What happens if a remote doctor makes a mistake in an emergency situation? Who’s responsible?
A: That’s a tough but critical question. Generally, the same medical malpractice laws apply to telehealth as to in-person care. If a remote doctor’s negligence directly leads to harm, they (and potentially the telehealth company) can be held liable.
However, proving negligence in telehealth can be more complex. Factors like the quality of the video connection, the accuracy of the patient’s self-reported information, and the limitations of remote examination can all play a role.
Let’s say a doctor misdiagnoses a rash over video chat because the image quality was poor. Proving that the misdiagnosis was due to negligence, rather than the inherent limitations of telehealth, could be tricky.
It’s always a good idea to check the telehealth provider’s insurance coverage and dispute resolution process beforehand. Also, make sure to document everything – consultations, diagnoses, and treatment plans – in case any issues arise down the line.
📚 References
Wikipedia Encyclopedia
구글 검색 결과
구글 검색 결과
구글 검색 결과
구글 검색 결과
구글 검색 결과